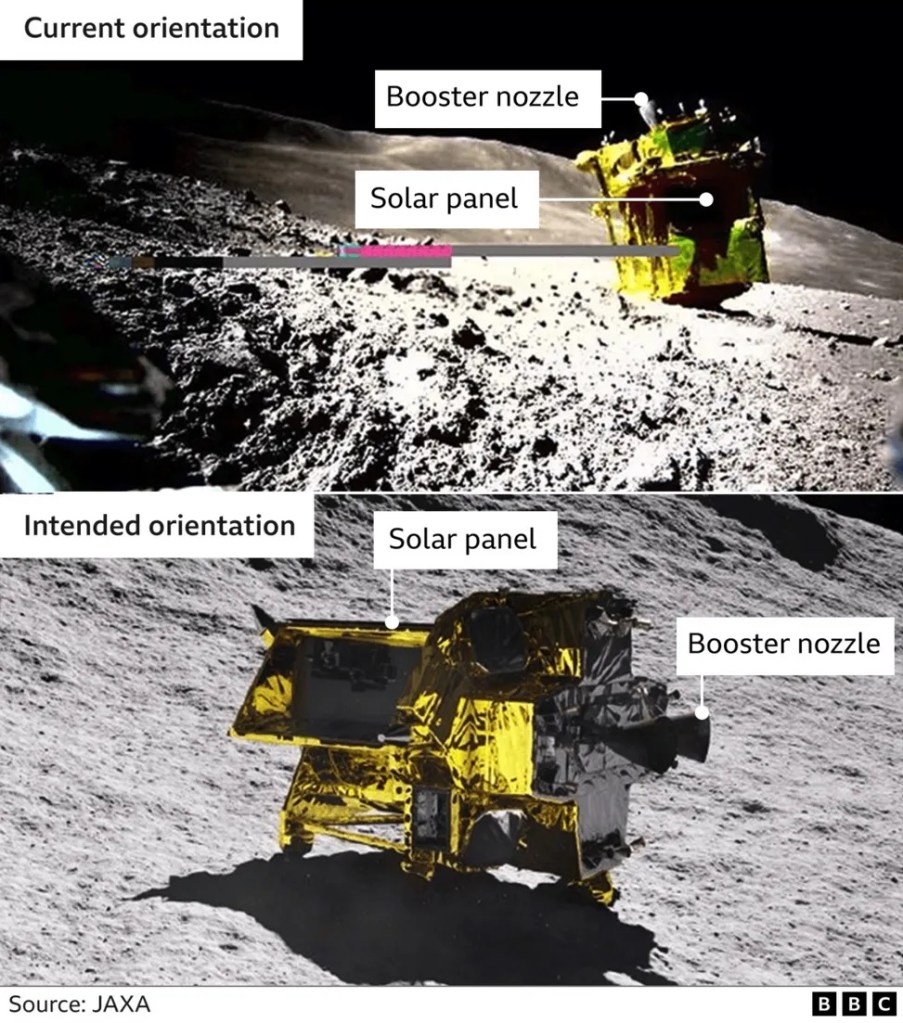
The craft is at a very awkward angle. A picture, captured by the small baseball-sized robot called Sora-Q – which was ejected from Slim moments before touchdown – showed the lander face-down on the lunar surface.
That left its solar panels facing away from the sunlight and unable to generate power. The decision was taken to put the lander into sleep mode – and conserve what power remained – less than three hours after it landed.
That tactic appears to have worked. A change in the direction of the sunlight has now “awoken” the craft.
https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-68131105
As previously reported, JAXA did achieve its goal of a “precision landing” — as some put it, a “pinpoint” touchdown within 100 meters of the intended target — within 55 meters, although if all had gone as planned, it would have been within 10 meters.
That’s far, far closer than previous Moon landings.
Too bad SLIM is essentially standing on its nose. But at least this is a beginning. Japan has now become the fifth country (US, USSR, China, India) to successfully “soft land” an object on the Moon.
And the robots it brought with it are pretty amazing. And tiny.