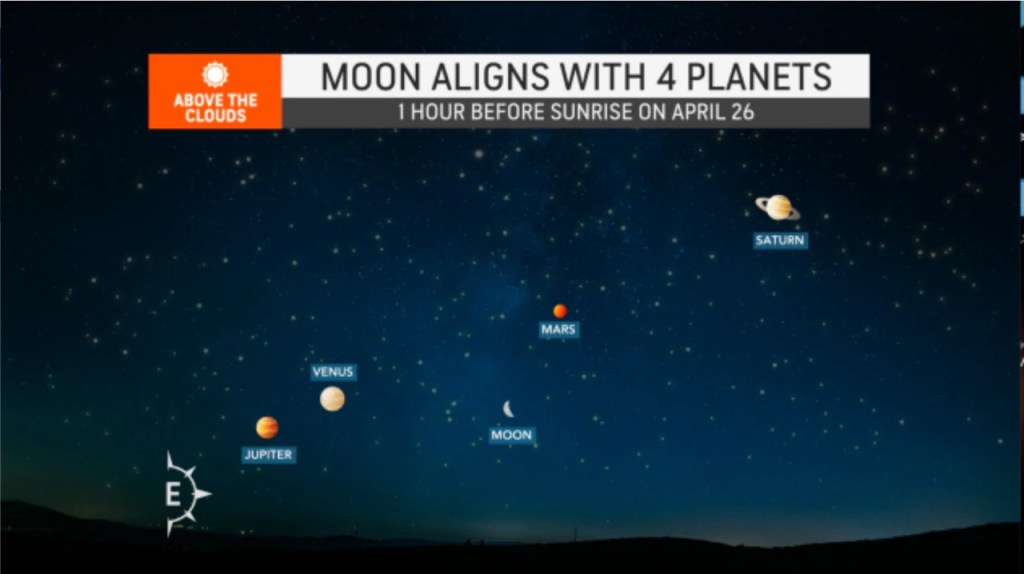
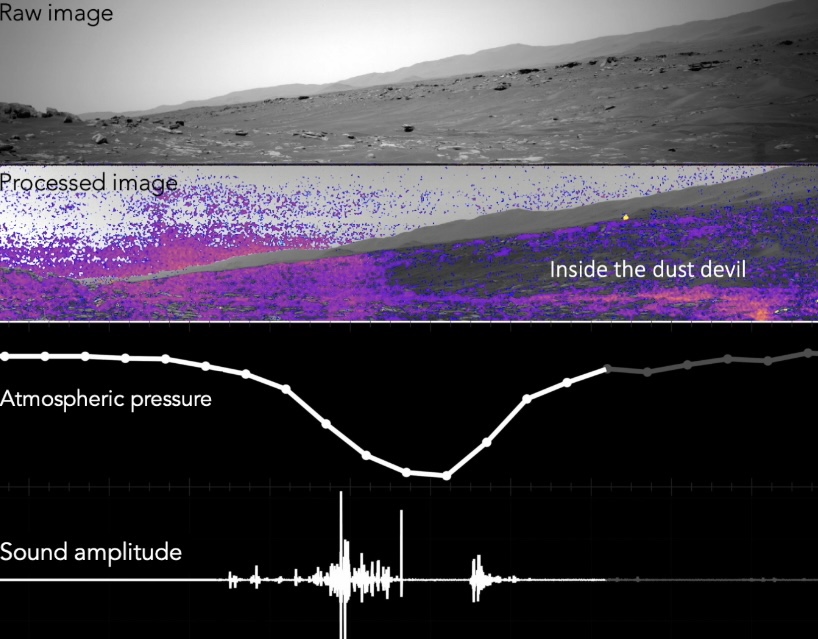
It was “definitely luck” that the dust devil appeared when it did, said the study’s lead author, who estimates there was just a 1-in-200 chance of capturing the audio.
https://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/mars-rover-captures-first-sound-dust-devil-red-planet-rcna61642
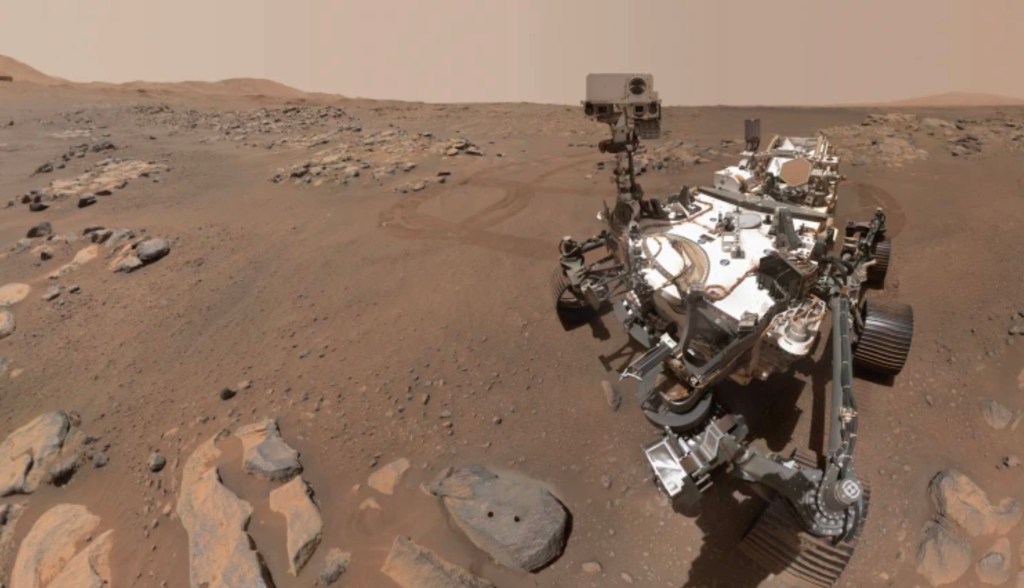
Perseverance has been on Mars for almost two years now, and already recorded wind on Mars for the first time in February 2021.
This dust devil was recorded in late September 2021 (wonder why only now it’s being revealed?). The dust devil was “average size,” which is described as about 400 feet / 122 meters tall and 80 feet / 24 meters wide, traveling at 16 feet / 5 meters per second (≈ 11 mph / 18 mph).
UPDATE. NBC incorrectly reported in the above linked article that the dust devil was recorded by Perseverance. It was actually recorded by InSight, which has just fallen silent after four years of operation. Sigh. I should get science news directly from the source and not from unreliable “news” sites.
https://jirafeau.isae-supaero.fr/f.php?h=2JWSkdJR&p=1
There are a lot of dust devils on Mars. A whole lot. Any settlement would have to be extremely prepared to deal with dust all the time, everywhere. If it ever got into equipment that regulated, say, breathable air inside habitats…